Scurvy: Understanding the Disease and Its Progressive Symptoms
Once considered a relic of the past, confined to tales of long sea voyages and historical deprivation, scurvy is unexpectedly making a modern resurgence. This nutritional deficiency, caused by a severe lack of vitamin C (ascorbic acid), can range from subtle, non-specific discomforts to life-threatening complications if left untreated. For anyone wondering, what is scurvy disease, it's essentially a breakdown in the body's ability to maintain healthy tissues, due to the absence of a vital nutrient it cannot produce on its own.
Understanding the early signs and how they progress is crucial for timely diagnosis and intervention, especially as recent cases highlight its unexpected presence in developed nations. This guide will walk you through the symptoms of scurvy, from its initial whispers to its more severe manifestations, and shed light on why recognizing them is more important now than ever.
What Is Scurvy Disease? The Crucial Role of Vitamin C
At its core, what is scurvy disease boils down to a profound deficiency of vitamin C. Our bodies are remarkable machines, but they lack the enzyme needed to synthesize vitamin C, meaning we must obtain it regularly through our diet. This nutrient is not just good for fighting colds; it's a cornerstone of numerous bodily functions.
Vitamin C is indispensable for the production of collagen, a protein that acts as the body's primary building block, vital for connective tissues, blood vessels, skin, bones, and teeth. Beyond collagen, vitamin C is a powerful antioxidant, supports robust immune function, and aids in the absorption of iron. When vitamin C levels plummet, these critical processes falter. Typically, symptoms of scurvy begin to appear around three months after a person consistently stops getting enough vitamin C in their diet.
The health implications of this deficiency are widespread: weakened blood vessels become fragile and prone to bleeding, wound healing is severely impaired, and the body's ability to fight off infections diminishes. The ripple effect across multiple systems explains the diverse and often confusing array of symptoms associated with scurvy.
The Early Whispers: Recognizing Initial Scurvy Symptoms
Catching scurvy in its early stages is key to preventing its progression. However, diagnosis can be challenging because many of the initial symptoms are non-specific and can mimic other conditions. These early signs are often the body's subtle cries for help:
- Fatigue and Weakness: A persistent feeling of tiredness and a lack of energy are among the first symptoms. This general malaise can be easily dismissed as stress or other common ailments, making it a tricky indicator.
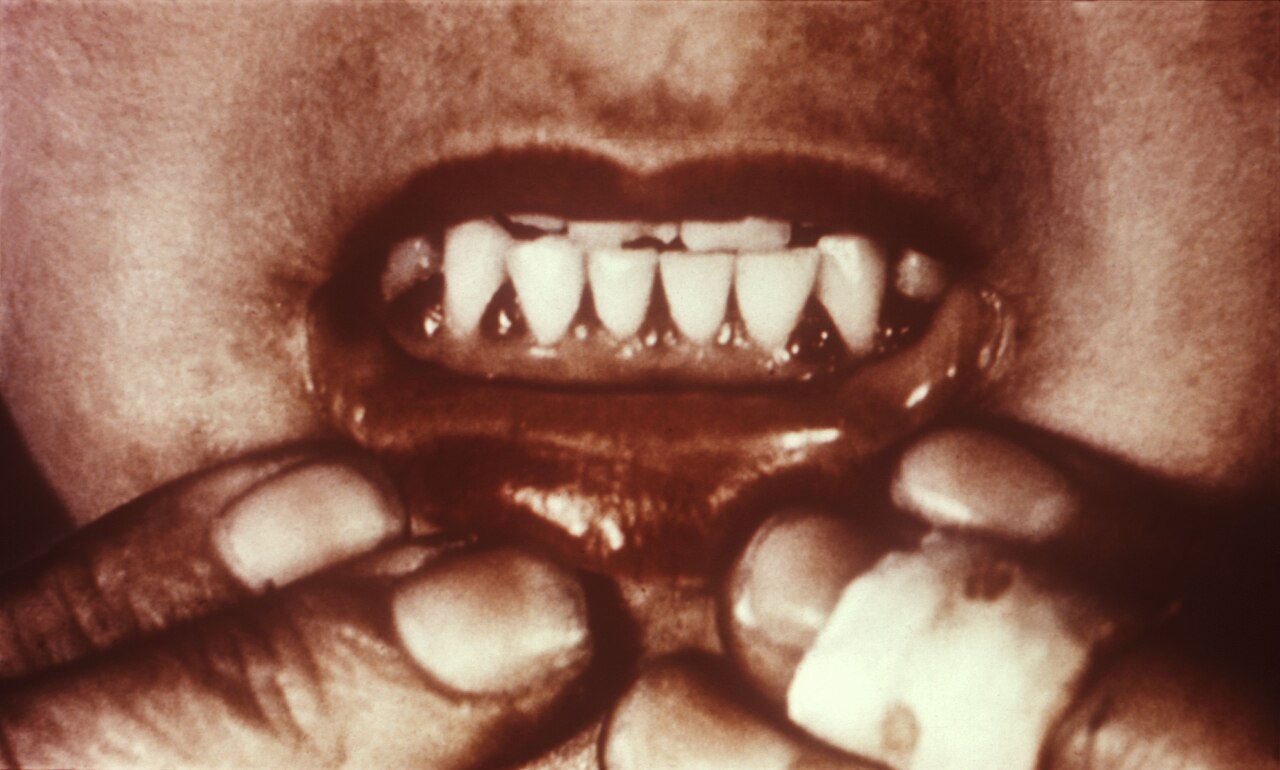
- Swollen, Bleeding Gums: This is one of the more classic and recognizable early signs. The gums may appear purplish, soft, and spongy, and bleed easily, even with gentle brushing or flossing. This is a direct consequence of weakened connective tissue in the oral cavity.
- Easy Bruising: Due to compromised blood vessel integrity, even minor bumps can lead to significant bruising (ecchymosis). This often manifests as reddish-purple spots on the skin, particularly on the legs, known as petechiae or purpura. These tiny spots are caused by small blood vessels leaking under the skin.
- Joint Pain: Aches and pains in the joints, sometimes accompanied by swelling, can occur. This is attributed to impaired collagen formation within the joint tissues.
- Slow Wound Healing: Cuts, scrapes, and even surgical incisions may take an unusually long time to heal, or may heal poorly, forming fragile scars. Old wounds might even reopen due to the body's inability to repair and maintain collagen.
If you or someone you know experiences a combination of these symptoms, especially alongside a diet lacking fresh fruits and vegetables, it's a strong signal to consult a healthcare professional. Early recognition can prevent much more severe complications.
When Scurvy Worsens: Progressive Signs and Complications
If left unaddressed, scurvy will inevitably progress, leading to increasingly severe and potentially life-threatening symptoms. These advanced signs demonstrate the profound systemic impact of long-term vitamin C deficiency:
Dental Problems
As the condition advances, the initial gum issues escalate dramatically. Weakened connective tissues can lead to teeth becoming loose and, in severe cases, even falling out. The gums become intensely swollen, painful, and prone to significant bleeding, making eating and speaking incredibly difficult. This dental degradation is a stark indicator of the body's inability to maintain essential structural proteins.
Skin Issues
The skin, a major collagen-dependent organ, suffers visibly. It can become rough, dry, and scaly. The characteristic reddish-purple spots (petechiae and purpura) become more widespread, especially on the legs, reflecting more extensive internal bleeding. In some severe instances, previously healed wounds or scars may spontaneously reopen, a chilling testament to the body's profound lack of repair capacity. Individuals may also present with diffuse petechiae and spontaneous thigh ecchymosis, accompanied by edema.
Internal Bleeding
Perhaps the most dangerous progression of scurvy is the development of internal hemorrhages. Weakened blood vessels throughout the body can rupture, leading to bleeding in various internal organs, muscles, and even the eyes. This internal bleeding can be life-threatening if not promptly diagnosed and treated. For example, muscular pain and swelling can indicate deeper bleeding into muscle tissue. Furthermore, cases have revealed alarmingly low levels of white blood cells in blood and urine, which are classic indicators of severe nutritional deficiency.
Scurvy's Modern Comeback: Why It Matters Today
The notion that scurvy belongs solely to history books is being challenged by a surprising resurgence in developed nations. Cases reported in countries like Australia and the United Kingdom have shocked medical communities, reminding us that no disease is truly "eradicated" as long as its root causes persist. For more insights into this phenomenon, you can read about Scurvy's Shocking Return: Modern Risks & How to Spot It.
This unexpected comeback is multifaceted, driven by a confluence of modern societal factors:
- Economic Hardship: Rising living costs and financial difficulties can force individuals to prioritize cheaper, calorie-dense foods over more expensive, nutrient-rich fresh fruits and vegetables, leading to severe vitamin C deprivation.
- Poor Dietary Choices: The pervasive presence of ultra-processed foods in modern diets, often devoid of essential vitamins and minerals, contributes significantly to nutritional deficiencies. A diet heavy in processed items but light on fresh produce is a recipe for nutrient gaps.
- Obesity and Malnutrition: Paradoxically, obesity can coexist with malnutrition. Individuals may consume an abundance of calories but still lack crucial vitamins and minerals, creating a scenario where someone is overfed yet undernourished.
- Social Isolation: Elderly individuals living alone are particularly vulnerable. They may neglect proper nutrition due to difficulty shopping, cooking, or simply a loss of appetite and motivation, increasing their risk of developing scurvy.
- Restrictive Eating Patterns & Unhealthy Habits: Children and older adults with very restrictive diets, perhaps due to allergies, picky eating, or misconceptions about healthy food, are at risk. Additionally, lifestyle factors like smoking and substance use disorders further deplete vitamin C reserves, increasing susceptibility.
These contributing factors underscore that what is scurvy disease in the 21st century is less about maritime adventures and more about systemic societal issues impacting dietary quality and access. To delve deeper into the reasons behind this unexpected return, explore Beyond Pirates: Unpacking Scurvy's Comeback in Developed Nations.
Prevention and Action: Safeguarding Your Health
The good news is that scurvy is entirely preventable and treatable. The key lies in a diet rich in vitamin C and prompt medical attention if symptoms arise.
Dietary Recommendations:
Ensure your diet includes plenty of vitamin C-rich foods. Excellent sources include:
- Citrus fruits: Oranges, grapefruits, lemons, limes.
- Berries: Strawberries, blueberries, raspberries.
- Bell peppers: Especially red and yellow varieties.
- Leafy greens: Kale, spinach.
- Broccoli and Brussels sprouts.
- Tomatoes, kiwi, and potatoes.
Even on a budget, incorporating these foods can be achieved through careful planning, purchasing seasonal produce, or opting for frozen varieties, which retain their nutritional value.
When to Seek Medical Attention:
If you experience persistent fatigue, unexplained bruising, bleeding gums, slow-healing wounds, or joint pain, especially if your diet has been consistently poor, do not hesitate to consult a doctor. Be prepared to discuss your dietary habits in detail. Diagnosis usually involves a review of your diet history, a physical examination, and potentially a blood test to measure your vitamin C levels.
Remember that because early symptoms can be non-specific, it's vital to provide your doctor with a comprehensive picture of your health and lifestyle. The treatment for scurvy is straightforward: vitamin C supplementation, which typically brings about a rapid recovery and reversal of symptoms.
Conclusion
Scurvy, a condition once relegated to historical footnotes, has re-emerged as a pertinent health concern in modern society. Understanding what is scurvy disease and its progressive symptoms—from fatigue and bleeding gums to severe skin issues and internal hemorrhages—is crucial for early detection and effective intervention. Its surprising return underscores the critical importance of a balanced, nutrient-rich diet in safeguarding overall health, even in affluent nations. By being aware of the signs and ensuring adequate vitamin C intake, we can collectively prevent this ancient affliction from taking hold in the present day. Prioritize your diet, listen to your body, and seek medical advice promptly if you suspect a deficiency.